Chronic Vision Loss
Astigmatism
Irregular shape of cornea
Both near and distance vision unclear
Myopia
Eye is too long
Distance vision unclear
Hyperopia
Eye is too short
Near vision unclear
Presbyopia:
Lens becomes more rigid with aging
Near vision unclear
Refractive Error
Age related opacification of the lens
Pathognomonic words/descriptors: white pupil reflex in adult
Presentation: Glare, halos, painless and bilateral blurry vision
Common Etiologies: Aging (most common), steroid use (ocular or systemic), diabetes
Treatment:
Cataract surgery
Cataracts
A leading cause of global blindness (“Silent thief of sight”)
Pathognomonic words/descriptors:
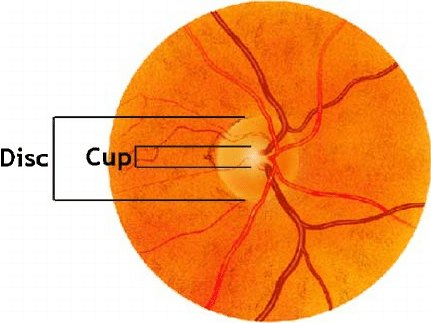
Elevated intraocular pressure, slow loss of peripheral vision, optic disc cupping/increased cup-to-disc ratio
Presentation: Insidious, gradual irreversible loss of peripheral vision associated with optic nerve changes. Associated with increased intraocular pressure (IOP>20)
Treatment:
Eyedrops to decrease aqueous humor production:
Alpha agonist, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Eyedrops to Increase aqueous humor outflow:
prostaglandin analogues
Laser/surgical trabeculoplasty
Open Angle Glaucoma
Leading cause of blindness >65 years in developed countries
Etiology - 2 Types:
Dry: slow progression with drusen deposition in the retina (due to complex lifestyle and genetic causes)
Wet: Rapid vision loss with fluid leakage due to choroidal neovascularization
Pathognomonic words/descriptors: Drusen in the retinal pigment epithelium, metamorphosia (straight lines appear wavy), abnormal Amsler grid test
Risk Factors: smoking, advanced age
Treatment: supportive, smoking cessation, vitamin supplementation (AREDs vitamins), anti-VEGF intravitreal injections for wet AMD.
Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Most common cause of blindness in age 25-74 in the US
2 Types:
Non-proliferative: microaneurysms, exudates, cotton wool spots, hemorrhages
Proliferative: neovascularization, macular edema, hemorrhages, retinal detachment
Risk Factors: diabetes duration, poor glucose control, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking
Treatment:
Diabetic control, laser photocoagulation, anti-VEGF injections, surgery in case of retinal detachment
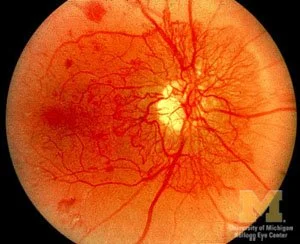
Diabetic Retinopathy
Normal retina on Left. Retina with features of diabetic retinopathy on right
Retinal Neovascularization, as can be seen in proliferative diabetic retinopathy